There’s a certain romance people attach to venture capital. Big checks. Fast growth. Headlines. But after a decade of covering startups up close, I’ve learned something quieter and far more impressive exists alongside that world.
Bootstrapped startups. These are companies built without outside investors. No safety net. No pressure to chase vanity metrics. Just customers, revenue, and a lot of discipline. And some of them didn’t just survive. They scaled to massive, global businesses.
Why Bootstrapping Still Matters in a VC-Obsessed World?
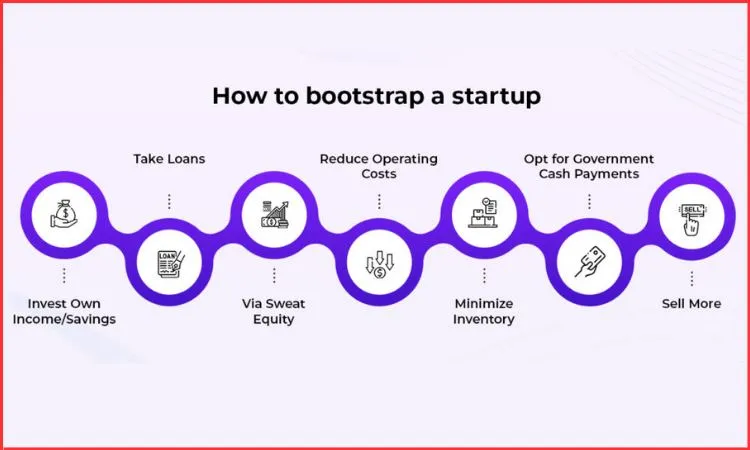
Raising money has never been easier. Or more tempting. But bootstrapping forces founders to answer hard questions early:
Read Also: Consumer Startups Winning Customer Loyalty
-
Will someone actually pay for this?
-
Does this solve a real problem?
-
Can this business sustain itself?
There’s no room to hide behind funding rounds.
That pressure sharpens decision-making. It also builds companies that last. Many of the biggest bootstrapped companies didn’t grow fast. They grew right.
What “Bootstrapped” Really Means in Practice?
Bootstrapping isn’t just “no investors.” It usually means:
-
Founders fund the early days themselves
-
Revenue comes before scale
-
Hiring happens slowly
-
Profitability matters early
It also means every decision hurts a little more. I’ve spoken to founders who delayed hiring for months just to keep cash flow healthy. That kind of constraint changes how you build.
The Myth That You Can’t Scale Without Investors
This myth refuses to die. Yes, venture capital can help you scale faster. But faster doesn’t always mean better. Some of the most respected software tools, SaaS platforms, and internet companies scaled globally with zero outside funding.
Not small lifestyle businesses. Real, durable companies.
Let’s talk about them.
Famous Bootstrapped Startups That Scaled Big
Basecamp
Basecamp is nearly continuously said to begin with, and for great reason. Built as a simple project management tool, it centered on clarity over complexity. No chasing undertaking bargains. No bloated features.
The authors prioritized calm development and productivity from day one. Years afterward, Basecamp got to be one of the most compelling bootstrapped program companies in the world.
Mailchimp
Mailchimp is a masterclass in patience. For a long time, it discreetly served little businesses whereas competitors chased subsidizing and features. The authors reinvested benefits, refined the item, and tuned in fanatically to customers.
Eventually, Mailchimp got to be so huge it was obtained for billions — without ever taking wander capital. That’s not good fortune. That’s teach.
Atlassian (Mostly Bootstrapped Early)
Atlassian famously started with customer revenue before raising capital much later. By the time investors came in, the company already had:
-
Product-market fit
-
Paying customers
-
A global footprint
They didn’t need money to survive. They used it to accelerate.
That difference matters.
GitHub (Bootstrapped Longer Than People Remember)
Before GitHub became a household name and raised funding, it was self-funded. The founders charged early. They focused on developers. They grew organically inside communities that mattered.
You Must Also Like: Emerging Startups to Watch This Year | Top New Companies
By the time capital entered the picture, the company already worked. That early bootstrapped phase shaped its culture.
Why Bootstrapped Software Companies Thrive?
Software and SaaS are especially friendly to bootstrapping.
Why?
-
Low marginal costs
-
Recurring revenue
-
Direct customer feedback loops
When done right, customers fund growth.
That creates a healthier relationship between product and user. You don’t build features to impress investors. You build features people will pay for.
I’ve seen bootstrapped founders scrap entire roadmaps because users didn’t care. That humility is rare in VC-backed environments.
Common Traits Across Successful Bootstrapped Startups
After a long time of interviews and case considers, designs begin to develop.
1. They Charge Early
Free items are enticing. Income is better.
Most bootstrapped startups start charging prior than VC-backed ones. Indeed little expenses approve demand.
Charging changes the relationship. Clients ended up accomplices, not fair clients.
2. They Grow Slower — On Purpose
Bootstrapped founders don’t chase hypergrowth. They chase sustainability.
Hiring is intentional. Marketing is tested slowly. Expansion happens when cash flow allows it.
This pace reduces risk and burnout.
3. They Obsess Over Profit Margins
Margins matter when there’s no external cash.
That forces better pricing, smarter infrastructure decisions, and fewer vanity features.
Ironically, this often leads to stronger long-term growth.
4. They Stay Close to Customers
Founders talk to users constantly.
Support tickets aren’t outsourced. Feedback isn’t filtered. Complaints are personal.
That closeness creates loyalty and sharper products.
A Real List of Bootstrapped Startups That Scaled Without Investors
Here’s a practical list of bootstrapped startups that scaled without investors, across industries:
-
Basecamp – Project management
-
Mailchimp – Email marketing
-
TechSmith – Screen recording software
-
Envato – Digital marketplaces
-
Zoho – Enterprise and SMB software
-
Shutterstock – Stock media (early bootstrapped phase)
-
GitLab – Open-source DevOps (bootstrapped early)
Each followed a different path, but all shared one thing: revenue first.
Bootstrapping vs VC: The Tradeoffs No One Talks About
Bootstrapping isn’t for everyone. It comes with tradeoffs:
-
Slower expansion
-
Limited resources
-
Founder financial risk
-
Fewer second chances
But venture capital has tradeoffs too:
-
Pressure to scale fast
-
Dilution of control
-
Misaligned incentives
-
Growth over sustainability
The best founders choose based on temperament, not trends.
Why Bootstrapped Startups Often Feel More Human?
This is something I’ve noticed again and again. Bootstrapped companies tend to:
-
Treat employees better
-
Avoid reckless layoffs
-
Build healthier cultures
-
Make long-term decisions
When there’s no external timeline forcing exits or growth curves, companies can breathe. That shows up in the product and the people.
How Bootstrapped Founders Think About Marketing?
Marketing without deep pockets forces creativity. Instead of massive ad spends, bootstrapped startups rely on:
-
Content that teaches
-
SEO done patiently
-
Community engagement
-
Word-of-mouth
It’s slower, but it compounds.
I’ve watched bootstrapped companies dominate niches simply by being helpful for years while competitors chased short-term traffic.
The Psychological Side of Bootstrapping
This part rarely gets discussed. Bootstrapping is emotionally intense. Every dollar feels personal. Every mistake costs more. There’s no investor to reassure you. But it also builds confidence.
When growth comes from customers, not checks, founders trust their instincts more. Decisions feel earned. That confidence stays even if the company later raises money.
When Bootstrapping Makes the Most Sense
Bootstrapping works especially well when:
-
You’re building for a niche market
-
You don’t need massive infrastructure upfront
-
You want control over direction
-
You value profitability over blitz-scaling
Many founders start bootstrapped and choose funding later — on their own terms. That flexibility is powerful.
Lessons From Bootstrapped Startups That Failed
Not all bootstrapped stories end well. Failures often come from:
-
Underpricing for too long
-
Founder burnout
-
Fear of hiring
-
Avoiding necessary risks
Bootstrapping isn’t about playing small. It’s about playing smart. Some founders hold onto control so tightly that growth stalls. Balance matters.
Why Bootstrapped Startups Are Having a Moment Again?
In recent years, market conditions changed. Capital became more expensive. Growth slowed. Layoffs followed. Suddenly, bootstrapped startups looked less old-fashioned and more resilient.
Profitability is back in fashion. And founders who learned to grow without investors are navigating uncertainty better than most.
A Personal Observation After Years Covering Startups
The loudest companies aren’t always the strongest. Some of the most impressive businesses I’ve seen were built quietly, over years, without press releases or funding announcements.
They focused on customers. On revenue. On building something useful. That’s the real lesson behind successful bootstrapped startups.
Final Thoughts From the Long View
Bootstrapping isn’t a badge of honor. It’s a strategy. For the right founders, it creates freedom, resilience, and businesses that don’t depend on market moods. The biggest bootstrapped companies didn’t reject investors out of ideology. They simply didn’t need them.
And that’s the point. If you want, I can break this down further by industry — SaaS, marketplaces, consumer apps, or solo-founder businesses — with examples and practical advice for each.